-
Property & Casualty
Property & Casualty Overview

Property & Casualty
We offer a full range of reinsurance products and the expertise of our talented reinsurance team.
Expertise
Publication
Biometric Information Privacy – Statutes, Claims and Litigation [Update]
Publication
Inflation – What’s Next for the Insurance Industry and the Policyholders it Serves?
Publication
Human Activity Generates Carbon and Warms the Atmosphere. Is Human Ingenuity Part of the Solution?
Publication
Illinois Changes Stance on Construction Defect Claims – The Trend Continues
Publication
Generative Artificial Intelligence in Insurance – Four Aspects of the Current Debate
Publication
Battered Umbrella – A Market in Urgent Need of Fixing -
Life & Health
Life & Health Overview

Life & Health
We offer a full range of reinsurance products and the expertise of our talented reinsurance team.

Publication
Underwriting High Net Worth Foreign Nationals – Considerations for U.S. Life Insurance Companies
Publication
Group Term Life Rate & Risk Management – Results of 2023 U.S. Survey
Publication
Trend Spotting on the Accelerated Underwriting Journey
Publication
All in a Day’s Work – The Impact of Non-Medical Factors in Disability Claims U.S. Industry Events
U.S. Industry Events
Publication
Marginal Gains in the Medicare Supplement Market -
Knowledge Center
Knowledge Center Overview

Knowledge Center
Our global experts share their insights on insurance industry topics.
Trending Topics -
About Us
About Us OverviewCorporate Information

Meet Gen Re
Gen Re delivers reinsurance solutions to the Life & Health and Property & Casualty insurance industries.
- Careers Careers
Individual Life Accelerated Underwriting – Summary Results of 2021 U.S. Survey

November 29, 2021
Nicole Conti
Region: North America
English
Gen Re is pleased to present summary results of our 2021 Individual Life Accelerated Underwriting Survey. Throughout this year, Gen Re collaborated with a steering committee of interested insurers to review the study framework. Much of the important feedback received during that process is reflected in the content detailed in the comprehensive report.
There were 43 Individual Life insurance carriers that participated in the study. (The full report was made available only to those participating companies.) Gen Re recognizes that insurers may be at varying stages of implementation with their Accelerated Underwriting workflow.
Survey Definition – Accelerated Underwriting
For the purpose of this study, Accelerated Underwriting (AU) refers to any Individual Life underwriting workflow that aims to decrease time from application to issue for applicants who meet criteria that qualifies them to bypass a paramedical exam and/or fluid collection. Programs may include some combination of the following:
- Collection of medical underwriting sources
- Collection of non‑medical data including credit attributes, motor vehicle records, etc.
- Expanded application/tele-interview process
- Fully automated and/or partially automated underwriting systems
Status of Accelerated Underwriting Workflow
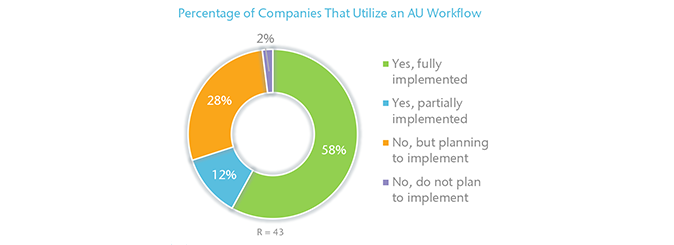
The majority of participating companies (70%) have either a fully implemented or partially implemented AU workflow; 28% do not currently utilize an AU workflow, but plan to implement one in the next two years. One company reported that it does not currently have, nor does it plan to implement an AU workflow at this time.
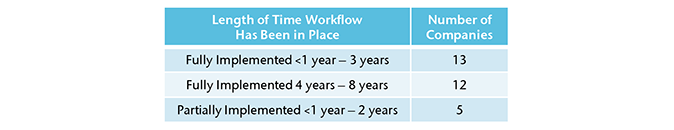
For those companies with fully implemented workflows, length of time a workflow has been in place ranged from less than one year up to eight years. Companies with partially implemented workflows have typically had pilot programs in place for less than two years.
Companies that do not currently utilize an AU workflow noted technology, budget constraints, staffing, and lack of product flexibility (i.e., only sell large face amount policies) as reasons they are unable to implement a program at this time.
Program Goals
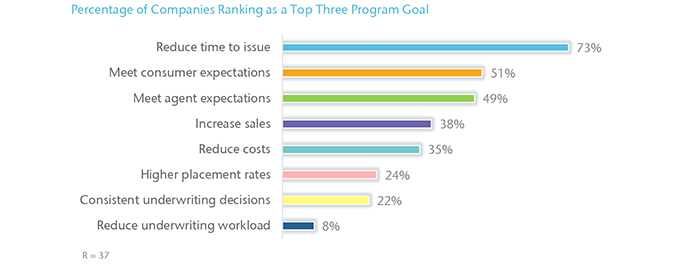
Nearly three quarters (73%) of companies cite reducing time to issue as one of the top three goals when implementing their AU workflow. Meeting consumer expectations and agent expectations also rank high among initial goals.
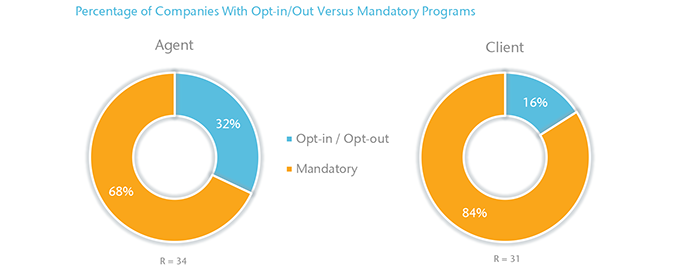
Opt‑in/Opt‑out Versus Mandatory Workflows
For many companies, an AU path is mandatory for both agents and clients if the application meets eligibility requirements. Some companies allow the agent and/or client to choose an AU path, though most systems automatically opt‑in an application, and require the agent to manually opt‑out if they wish to do so.
Agent Reactions to Accelerated Underwriting Workflow
Overall, companies have received positive feedback from agents around their AU workflow. For most, AU is their preferred path because of its convenience. However, agents are dissatisfied with some areas of AU. Of note, agents would like to see higher face amounts, additional product offerings, and higher throughput percentages. Agents having little-to‑no experience with AU are slower to adjust to an accelerated process. Many of these agents would rather go through the process of ordering a medical exam to receive the best possible rate class for the end customer.
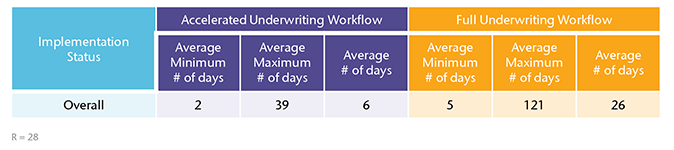
Underwriting Decision Time
On average, companies that have an AU workflow see an improvement of 20 business days from application submission to final decision compared to full underwriting workflows.
Underwriting Rate Classes
Companies typically offer four underwriting rate classes through their AU program. The number of rate classes ranged from a low of one to a high of eight.
Approximately 31% of companies offer smoker rates through their AU workflows. Those that offer smoker rates typically offer two rate classes: preferred smoker and standard smoker.
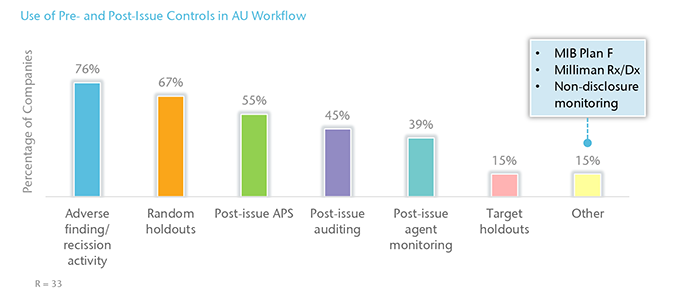
Pre‑and Post‑Issue Controls
Most companies (76%) use adverse finding/recission activity as a control measure throughout their AU workflow. Other common controls in place include random holdouts (67%), post‑issue APS (55%), and post‑issue auditing (45%).
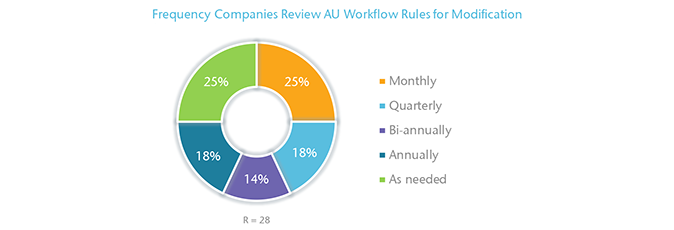
Modification of Rules
The frequency with which companies review their AU workflow rules varies. One quarter of participating companies review their rules monthly. Another 25% review them on an as needed basis. A few companies note that they conduct review processes on an annual or bi‑annually basis.
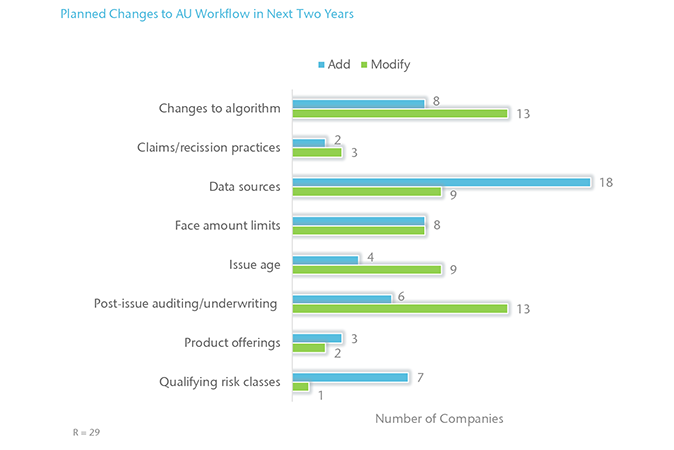
Planned Changes to Workflow
The most prevalent planned changes to AU workflows in the next two years include the addition of data sources, modifications to algorithms, and modifications to post‑issue auditing/underwriting procedures.
None of the companies reported plans to remove elements of their AU workflow.
Download the PDF version for a list of participating companies.





